Healthy Diet
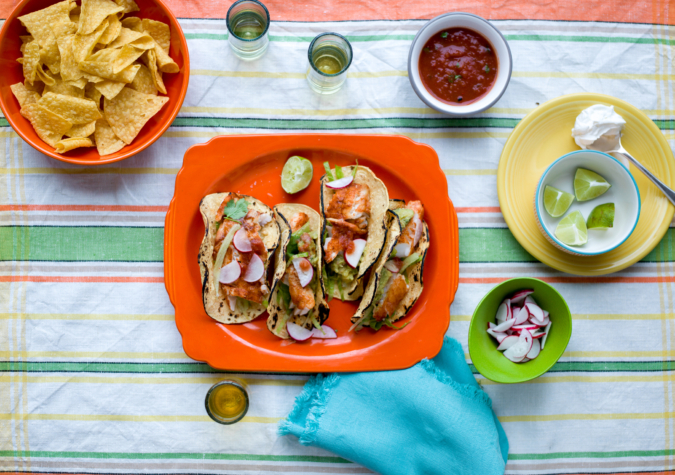

What do all of today’s diets have in common? Seafood
Whether you follow one diet strictly, or find balance in following multiple, seafood is the common key protein in your diet!
Find out how Alaska seafood is the perfect fit in all these diets:
-
Pescatarian
-
Wild Alaska seafood is loaded omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin B12, with many types also being rich in vitamin D and zinc which can be common deficiencies in pescatarian diets.
-
Gluten Free
-
Gluten free diets can often be deficient in nutrients such as vitamin D, selenium, and calcium. Including Wild Alaska seafood can help to ensure adequate intake of these valuable nutrients.
-
Mediterranean
-
Wild Alaska seafood is a source of high-quality protein that contributes essential omega-3 fatty acids such as EPA and DHA, found exclusively in marine species. Wild Alaska seafood also provides nutrients such as vitamin D, B vitamins, selenium, zinc, and many more.
-
Paleo
-
Wild Alaska seafood is a source of high-quality protein that provides vital nutrients for a Paleo diet such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin B12, selenium, and vitamin D. Canned salmon with bones is an good source of calcium, which can often be deficient in paleo diets.
-
Keto
-
Wild Alaska seafood provides vital nutrients for people following a ketogenic diet such as omega-3 fatty acids, lean protein, vitamin B12, vitamin D, and selenium. Additionally, canned wild Alaska salmon with bones is a good source of calcium.
-
Dash
-
Wild Alaska seafood is low in sodium, saturated fat and trans-fat, and high in heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids. Alaska seafood also provides lean protein, potassium, calcium, vitamin D, selenium, and vitamin B12.
-
Flexitarian
-
Wild Alaska seafood provides key nutrients for diets where meat is eaten occasionally. These include lean protein, essential omega-3 fatty acids, calcium, zinc, vitamin D, and vitamin B12. Consume 4-ounces of wild Alaska seafood twice per week.
-
Volumetrics
-
Wild Alaska seafood that is low in fat and calories is a nutrient-dense and satisfying addition to this eating pattern. Wild Alaska seafood such as cod, pollock, rockfish, sole/flounder, crab, and more provide lean protein, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin B12, selenium, and potassium.
-
Mayo Clinic
-
Wild Alaska seafood is a lean source of satisfying protein high in omega-3 fatty acids and low in saturated fat. It also contributes vital nutrients such as selenium, vitamin B12, and vitamin D.
-
Nordic
-
Wild Alaska seafood favorites of this diet include salmon and herring for their rich omega-3 fatty acid content and quality protein. Alaska seafood also provides vitamin D, B vitamins, selenium, potassium, and zinc.
-
TLC
-
Wild Alaska seafood contains nutrients to support optimal heart health, such as omega-3 fatty acids. It also provides lean protein, vitamin D, B vitamins, selenium, potassium, and zinc. Eat 4-ounces of fatty fish twice per week, for people both with and without coronary heart disease.
