Immune Function
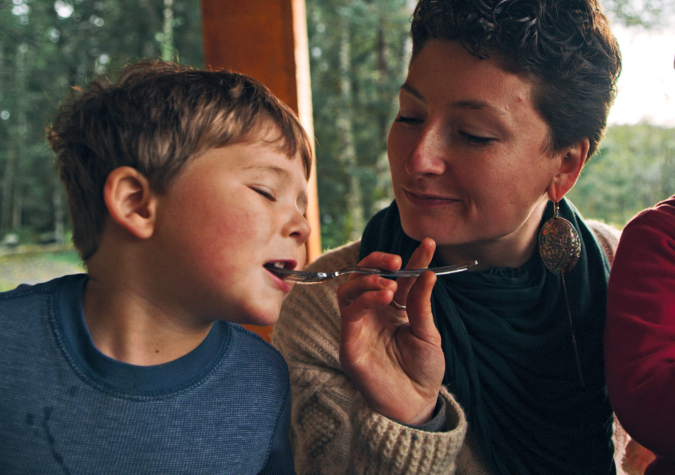

Alaska Seafood & Immune Function
Whether you’re young or old, seafood omega-3s may tone down overactive immune responses, making your symptoms of inflammation less severe.
For example, seafood omega-3s may promote immune system maturation in infancy and lessen the symptoms of childhood allergies or delay their onset. Research also suggests that increased omega-3 consumption may ease the symptoms of some inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, certain allergies and digestive disorders.
Nutrients Associated with Wild Alaska Seafood and Immunity
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
-
Omega-3 fatty acids are well known for their anti-inflammatory properties, but evidence also supports that omega-3 fatty acids are an essential component of a healthy immune system. [1] Omega 3 fatty acids have the ability to generate specialized pro-solving lipid mediators (SPMs), which play an important function in downregulating the immune response and resolving inflammation after the body’s immune system has performed its purpose.
Wild Alaska seafood is an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, especially salmon, sablefish, salmon and herring. Current guidelines recommend that Americans consume 8-ounces of seafood per week in order to consume adequate amounts.
-
Zinc
-
Zinc plays a critical role in host defenses against infections and deficiency will often result in suppressed immune function. Most people consuming a typical Western diet do not consume adequate amounts of zinc and should consider increasing zinc-rich food sources in their diet.
Oysters are one of the world’s greatest sources of zinc, providing 291% of the daily value. Other Alaska seafood such as crab, clams, mussels, and shrimp are also rich in zinc and are considered to be good sources.
-
Selenium
-
Selenium is one of the most crucial nutrients for maintaining and improving immune function. It provides powerful antioxidant protection to the body via the selenium containing enzyme, glutathione peroxidase. This antioxidant helps to reduce oxidative stress and to minimize damaging free radicals in the body.
Wild Alaska seafood, including halibut, rockfish and salmon, is one of the best food sources of selenium and is considered to be an excellent source of selenium.
Selenium RDA (Recommended Daily Allowance or Daily Value) = 55mcg
- 3 oz rockfish has 65 mcg or 118% DV (daily value)
- 3 oz Razor clam has 54 mcg, or 99% DV
- 3 oz Dungeness has 41 mcg, or 75% DV (king and snow crab are also very high, 34 and 38 mcg respectively)
- 3 oz halibut has 47 mcg or 85% DV
- 3 oz of both king and keta salmon have 40 mcg, or 73% DV
-
Vitamin D
-
Vitamin D plays a role in the immune response to infection by triggering the production of a peptide that exerts antimicrobial activity against intracellular bacteria. [2] Low vitamin D status, which is common in the United States, increases susceptibility to infection. [3] Wild Alaska seafood is one of the few food sources of this nutrient that is so important for immune function.
All forms of wild Alaska seafood including all varieties of salmon and white fish are considered to be excellent sources.
Vitamin D RDA =600 IU (15 mcg)
- 3 oz Serving of Coho Salmon has 383 IU (9.6mcg), or 64% of RDA (DV)
- 3 oz Sockeye has 14.2 mcg, or 95% DV
- 3 oz Pink Salmon has 11mcg, or 73% DV
- 3 oz Halibut has 5mcg or 33% DV
-
Vitamin A
-
Vitamin A plays a role in immune function and enhances the capacity of epithelial tissue to resist invasion by pathogenic bacteria. [4] Foods such as deep orange or red vegetables are traditionally considered when considering vitamin A food sources. However, seafood can also contribute Vitamin A to the diet.
Alaska sea cucumber is an excellent source, and razor clams and rockfish are considered to be good sources.
-
Glutamine
-
Glutamine is an amino acid that is found in greater quantities in the body than any other amino acid. It is crucial for maintaining optimal antioxidant status, intestinal health, and is known for powering immune cells. [5] Alaska seafood is a good source of glutamine.
-
Other Nutrients
-
Other nutrients to support immunity include Vitamin E, Vitamin A, vitamin C, prebiotics and probiotics and other antioxidants such as N-acetyl cysteine and alpha-lipoic acid.
